فشل الكبد
| فشل الكبد | |
|---|---|
| تصنيف وموارد خارجية | |
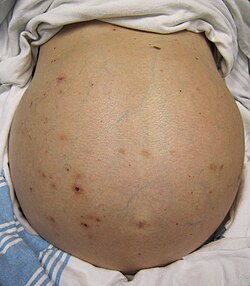 A person with massive ascites and caput medusae due to cirrhotic liver failure | |
| ت.د.أ.-10 | K72.9 |
| ق.ب.الأمراض | 5728 |
| إي ميديسين | med/990 |
| ن.ف.م.ط. | [1] |
| تعديل |
|
فشل الكبد هو عجز الكبد عن أداء وظيفته التصنيعية ووظيفته الاستقلابية بشكل طبيعي، وتم التعرف على نوعين من الفشل (الحاد والمزمن).[1]
ملاحظة: المقال يحتاج لإتمام ترجمة وتوسع ..
فشل الكبد الحاد
Acute liver failure is defined as "the rapid development of hepatocellular dysfunction, specifically coagulopathy and mental status changes (encephalopathy) in a patient without known prior liver disease".[2]:1557
The diagnosis of acute liver failure is based on physical exam, laboratory findings, patient history, and past medical history to establish mental status changes, coagulopathy, rapidity of onset, and absence of known prior liver disease respectively.[2]:1557
The exact definition of "rapid" is somewhat questionable, and different sub-divisions exist which are based on the time from onset of first hepatic symptoms to onset of encephalopathy. One scheme defines "acute hepatic failure" as the development of encephalopathy within 26 weeks of the onset of any hepatic symptoms. This is sub-divided into "fulminant hepatic failure", which requires onset of encephalopathy within 8 weeks, and "subfulminant", which describes onset of encephalopathy after 8 weeks but before 26 weeks.[3] Another scheme defines "hyperacute" as onset within 7 days, "acute" as onset between 7 and 28 days, and "subacute" as onset between 28 days and 24 weeks.[2]:1557
فشل الكبد المزمن
Chronic liver failure usually occurs in the context of cirrhosis, itself potentially the result of many possible causes, such as excessive alcohol intake, hepatitis B or C, autoimmune, hereditary and metabolic causes (such as iron or copper overload, Steatohepatitis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease).
مراجع
- ↑ O'Grady JG, Schalm SW, Williams R (1993). "Acute liver failure: redefining the syndromes". Lancet. 342 (8866): 273–5. PMID 8101303. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)91818-7.
- ↑ تعدى إلى الأعلى ل: 2٫0 2٫1 2٫2 Sleisenger, edited by Mark Feldman, Lawrence S. Friedman, Lawrence J. Brandt; consulting editor, Marvin H. (2009). Sleisenger & Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease pathophysiology, diagnosis, management (PDF) (9th ed. ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: MD Consult. ISBN 978-1-4160-6189-2.
- ↑ Sood, Gagan K. "Acute Liver Failure". Mescape. Retrieved 14 December 2011.
